UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-Q
(Mark One)
|
☒ |
QUARTERLY REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the quarterly period ended June 30, 2017
|
☐ |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from _____________ to ___________
Commission File Number 1-8462
GRAHAM CORPORATION
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
16-1194720 |
|
(State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
|
|
|
20 Florence Avenue, Batavia, New York |
14020 |
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
(Zip Code) |
585-343-2216
(Registrant's telephone number, including area code)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes ☒ No ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See definition of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer," "smaller reporting company," and "emerging growth company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
|
Large accelerated filer |
☐ |
|
Accelerated filer |
☒ |
|
Non-accelerated filer |
☐ |
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company |
☐ |
|
Emerging growth company |
☐ |
|
|
|
If an emerging growth company, indicate by check mark if the registrant has elected not to use the extended transition period for complying with any new or revised financial accounting standards provided pursuant to Section 13(a) of the Exchange Act. ☐
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
Yes ☐ No ☒
As of August 2, 2017, there were outstanding 9,768,686 shares of the registrant’s common stock, par value $.10 per share.
Graham Corporation and Subsidiaries
Index to Form 10-Q
As of June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017 and for the Three-Month Periods Ended June 30, 2017 and 2016
|
|
|
Page |
|
Part I. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 1. |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 2. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
Item 3. |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 4. |
21 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Part II. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 2. |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 5. |
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Item 6. |
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
24 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
||
2
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
FORM 10-Q
JUNE 30, 2017
PART I – FINANCIAL INFORMATION
3
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME AND RETAINED EARNINGS
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(Amounts in thousands, except per share data) |
|
|||||
|
Net sales |
|
$ |
20,851 |
|
|
$ |
22,365 |
|
|
Cost of products sold |
|
|
15,985 |
|
|
|
18,254 |
|
|
Gross profit |
|
|
4,866 |
|
|
|
4,111 |
|
|
Other expenses and income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Selling, general and administrative |
|
|
3,623 |
|
|
|
3,598 |
|
|
Selling, general and administrative – amortization |
|
|
58 |
|
|
|
58 |
|
|
Restructuring charge |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
555 |
|
|
Interest income |
|
|
(151 |
) |
|
|
(87 |
) |
|
Interest expense |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
Total other expenses and income |
|
|
3,533 |
|
|
|
4,126 |
|
|
Income before provision for income taxes |
|
|
1,333 |
|
|
|
(15 |
) |
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
398 |
|
|
|
(100 |
) |
|
Net income |
|
|
935 |
|
|
|
85 |
|
|
Retained earnings at beginning of period |
|
|
110,544 |
|
|
|
109,013 |
|
|
Dividends |
|
|
(879 |
) |
|
|
(866 |
) |
|
Retained earnings at end of period |
|
$ |
110,600 |
|
|
$ |
108,232 |
|
|
Per share data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.01 |
|
|
Diluted: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.01 |
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basic |
|
|
9,748 |
|
|
|
9,675 |
|
|
Diluted |
|
|
9,758 |
|
|
|
9,680 |
|
|
Dividends declared per share |
|
$ |
0.09 |
|
|
$ |
0.09 |
|
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
4
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
|
|
(Amounts in thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Net income |
|
$ |
935 |
|
|
$ |
85 |
|
|
Other comprehensive income: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Foreign currency translation adjustment |
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
(138 |
) |
|
Defined benefit pension and other postretirement plans net of income tax of $93 and $123, for the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively |
|
|
170 |
|
|
|
225 |
|
|
Total other comprehensive income |
|
|
224 |
|
|
|
87 |
|
|
Total comprehensive income |
|
$ |
1,159 |
|
|
$ |
172 |
|
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
5
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2017 |
|
||
|
|
|
(Amounts in thousands, except per share data) |
|
|||||
|
Assets |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
25,260 |
|
|
$ |
39,474 |
|
|
Investments |
|
|
50,000 |
|
|
|
34,000 |
|
|
Trade accounts receivable, net of allowances ($167 and $168 at June 30 and March 31, 2017, respectively) |
|
|
11,213 |
|
|
|
11,483 |
|
|
Unbilled revenue |
|
|
11,459 |
|
|
|
15,842 |
|
|
Inventories |
|
|
7,909 |
|
|
|
9,246 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
|
|
910 |
|
|
|
681 |
|
|
Total current assets |
|
|
106,751 |
|
|
|
110,726 |
|
|
Property, plant and equipment, net |
|
|
16,646 |
|
|
|
17,021 |
|
|
Prepaid pension asset |
|
|
2,579 |
|
|
|
2,340 |
|
|
Goodwill |
|
|
6,938 |
|
|
|
6,938 |
|
|
Permits |
|
|
10,300 |
|
|
|
10,300 |
|
|
Other intangible assets, net |
|
|
4,023 |
|
|
|
4,068 |
|
|
Other assets |
|
|
294 |
|
|
|
177 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
147,531 |
|
|
$ |
151,570 |
|
|
Liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Current portion of capital lease obligations |
|
$ |
107 |
|
|
$ |
107 |
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
7,142 |
|
|
|
10,295 |
|
|
Accrued compensation |
|
|
4,327 |
|
|
|
5,189 |
|
|
Accrued expenses and other current liabilities |
|
|
3,126 |
|
|
|
3,723 |
|
|
Customer deposits |
|
|
12,510 |
|
|
|
12,407 |
|
|
Income taxes payable |
|
|
389 |
|
|
|
317 |
|
|
Total current liabilities |
|
|
27,601 |
|
|
|
32,038 |
|
|
Capital lease obligations |
|
|
118 |
|
|
|
143 |
|
|
Deferred income tax liability |
|
|
4,353 |
|
|
|
4,051 |
|
|
Accrued pension liability |
|
|
489 |
|
|
|
467 |
|
|
Accrued postretirement benefits |
|
|
767 |
|
|
|
761 |
|
|
Total liabilities |
|
|
33,328 |
|
|
|
37,460 |
|
|
Commitments and contingencies (Note 11) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Preferred stock, $1.00 par value, 500 shares authorized |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Common stock, $.10 par value, 25,500 shares authorized 10,580 and 10,548 shares issued and 9,766 and 9,740 shares outstanding at June 30 and March 31, 2017, respectively |
|
|
1,058 |
|
|
|
1,055 |
|
|
Capital in excess of par value |
|
|
23,105 |
|
|
|
23,176 |
|
|
Retained earnings |
|
|
110,600 |
|
|
|
110,544 |
|
|
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
(8,210 |
) |
|
|
(8,434 |
) |
|
Treasury stock (814 and 808 shares at June 30 and March 31, 2017, respectively) |
|
|
(12,350 |
) |
|
|
(12,231 |
) |
|
Total stockholders’ equity |
|
|
114,203 |
|
|
|
114,110 |
|
|
Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
|
$ |
147,531 |
|
|
$ |
151,570 |
|
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
6
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(Unaudited)
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Operating activities: |
|
(Dollar amounts in thousands) |
|
|||||
|
Net income |
|
$ |
935 |
|
|
$ |
85 |
|
|
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Depreciation |
|
|
497 |
|
|
|
524 |
|
|
Amortization |
|
|
58 |
|
|
|
58 |
|
|
Amortization of unrecognized prior service cost and actuarial losses |
|
|
263 |
|
|
|
348 |
|
|
Stock-based compensation (income) expense |
|
|
(67 |
) |
|
|
42 |
|
|
Loss (gain) on disposal or sale of property, plant and equipment |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
1 |
|
|
Deferred income taxes |
|
|
185 |
|
|
|
106 |
|
|
(Increase) decrease in operating assets: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts receivable |
|
|
276 |
|
|
|
(3,511 |
) |
|
Unbilled revenue |
|
|
4,394 |
|
|
|
(1,868 |
) |
|
Inventories |
|
|
1,338 |
|
|
|
3,560 |
|
|
Prepaid expenses and other current and non-current assets |
|
|
(334 |
) |
|
|
(792 |
) |
|
Income taxes payable |
|
|
72 |
|
|
|
(214 |
) |
|
Prepaid pension asset |
|
|
(239 |
) |
|
|
— |
|
|
Increase (decrease) in operating liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Accounts payable |
|
|
(3,170 |
) |
|
|
(1,011 |
) |
|
Accrued compensation, accrued expenses and other current and non-current liabilities |
|
|
(1,462 |
) |
|
|
(115 |
) |
|
Customer deposits |
|
|
101 |
|
|
|
6,694 |
|
|
Long-term portion of accrued compensation, accrued pension liability and accrued postretirement benefits |
|
|
29 |
|
|
|
(93 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
|
2,876 |
|
|
|
3,814 |
|
|
Investing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Purchase of property, plant and equipment |
|
|
(117 |
) |
|
|
(129 |
) |
|
Purchase of investments |
|
|
(25,000 |
) |
|
|
(9,000 |
) |
|
Redemption of investments at maturity |
|
|
9,000 |
|
|
|
9,000 |
|
|
Net cash used by investing activities |
|
|
(16,117 |
) |
|
|
(129 |
) |
|
Financing activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Principal repayments on capital lease obligations |
|
|
(24 |
) |
|
|
(11 |
) |
|
Issuance of common stock |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
4 |
|
|
Dividends paid |
|
|
(879 |
) |
|
|
(866 |
) |
|
Purchase of treasury stock |
|
|
(119 |
) |
|
|
(30 |
) |
|
Excess tax deficiency on stock awards |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(35 |
) |
|
Net cash used by financing activities |
|
|
(1,022 |
) |
|
|
(938 |
) |
|
Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
(114 |
) |
|
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
|
|
(14,214 |
) |
|
|
2,633 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
|
|
39,474 |
|
|
|
24,072 |
|
|
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
|
$ |
25,260 |
|
|
$ |
26,705 |
|
See Notes to Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
7
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONDENSED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(Unaudited)
(Amounts in thousands, except per share data)
NOTE 1 – BASIS OF PRESENTATION:
Graham Corporation's (the "Company's") Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements include its (i) wholly-owned foreign subsidiary located in Suzhou, China and (ii) wholly-owned domestic subsidiary located in Lapeer, Michigan. The Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the U.S. ("GAAP") for interim financial information and the instructions to Form 10-Q and Rule 10-01 of Regulation S-X, each as promulgated by the Securities and Exchange Commission. The Company's Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements do not include all information and notes required by GAAP for complete financial statements. The unaudited Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2017 presented herein was derived from the Company’s audited Consolidated Balance Sheet as of March 31, 2017. For additional information, please refer to the consolidated financial statements and notes included in the Company's Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 ("fiscal 2017"). In the opinion of management, all adjustments, including normal recurring accruals considered necessary for a fair presentation, have been included in the Company's Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
The Company's results of operations and cash flows for the three months ended June 30, 2017 are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected for the current fiscal year, which ends March 31, 2018 ("fiscal 2018").
NOTE 2 – REVENUE RECOGNITION:
The Company recognizes revenue on all contracts with a planned manufacturing process in excess of four weeks (which approximates 575 direct labor hours) using the percentage-of-completion method. The majority of the Company's revenue is recognized under this methodology. The Company has established the systems and procedures essential to developing the estimates required to account for contracts using the percentage-of-completion method. The percentage-of-completion method is determined by comparing actual labor incurred to a specific date to management's estimate of the total labor to be incurred on each contract or completion of operational milestones assigned to each contract. Contracts in progress are reviewed monthly by management, and sales and earnings are adjusted in current accounting periods based on revisions in the contract value and estimated costs at completion. Losses on contracts are recognized immediately when evident to management.
Revenue on contracts not accounted for using the percentage-of-completion method is recognized utilizing the completed contract method. The majority of the Company's contracts (as opposed to revenue) have a planned manufacturing process of less than four weeks and the results reported under this method do not vary materially from the percentage-of-completion method. The Company recognizes revenue and all related costs on these contracts upon substantial completion or shipment to the customer. Substantial completion is consistently defined as at least 95% complete with regard to direct labor hours. Customer acceptance is generally required throughout the construction process and the Company has no further material obligations under its contracts after the revenue is recognized.
Receivables billed but not paid under retainage provisions in the Company’s customer contracts were $873 and $971 at June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017, respectively.
NOTE 3 – INVESTMENTS:
Investments consist of certificates of deposits with financial institutions. All investments have original maturities of greater than three months and less than one year and are classified as held-to-maturity, as the Company believes it has the intent and ability to hold the securities to maturity. Investments are stated at amortized cost which approximates fair value. All investments held by the Company at June 30, 2017 are scheduled to mature on or before May 15, 2018.
8
NOTE 4 – INVENTORIES:
Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or market, using the average cost method. Unbilled revenue in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets represents revenue recognized that has not been billed to customers on contracts accounted for on the percentage-of-completion method. For contracts accounted for on the percentage-of-completion method, progress payments are netted against unbilled revenue to the extent the payment is less than the unbilled revenue for the applicable contract. Progress payments exceeding unbilled revenue are netted against inventory to the extent the payment is less than or equal to the inventory balance relating to the applicable contract, and the excess is presented as customer deposits in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Major classifications of inventories are as follows:
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2017 |
|
||
|
Raw materials and supplies |
|
$ |
2,936 |
|
|
$ |
3,016 |
|
|
Work in process |
|
|
9,351 |
|
|
|
12,573 |
|
|
Finished products |
|
|
997 |
|
|
|
891 |
|
|
|
|
|
13,284 |
|
|
|
16,480 |
|
|
Less - progress payments |
|
|
5,375 |
|
|
|
7,234 |
|
|
Total |
|
$ |
7,909 |
|
|
$ |
9,246 |
|
NOTE 5 – INTANGIBLE ASSETS:
Intangible assets are comprised of the following:
|
|
|
Gross Carrying Amount |
|
|
Accumulated Amortization |
|
|
Net Carrying Amount |
|
|||
|
At June 30, 2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intangibles subject to amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
$ |
2,700 |
|
|
$ |
1,177 |
|
|
$ |
1,523 |
|
|
Intangibles not subject to amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Permits |
|
$ |
10,300 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
10,300 |
|
|
Tradename |
|
|
2,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,500 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
12,800 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
12,800 |
|
|
At March 31, 2017 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Intangibles subject to amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Customer relationships |
|
$ |
2,700 |
|
|
$ |
1,132 |
|
|
$ |
1,568 |
|
|
Intangibles not subject to amortization: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Permits |
|
$ |
10,300 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
10,300 |
|
|
Tradename |
|
|
2,500 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
2,500 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
12,800 |
|
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
12,800 |
|
Intangible assets are amortized on a straight line basis over the estimated useful lives. Intangible amortization expense for each of the three-month periods ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 was $45. As of June 30, 2017, amortization expense is estimated to be $135 for the remainder of fiscal 2018 and $180 in each of the fiscal years ending March 31, 2019, 2020, 2021 and 2022.
NOTE 6 – STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION:
The Amended and Restated 2000 Graham Corporation Incentive Plan to Increase Shareholder Value, as approved by the Company’s stockholders at the Annual Meeting on July 28, 2016, provides for the issuance of up to 1,375 shares of common stock in connection with grants of incentive stock options, non-qualified stock options, stock awards and performance awards to officers, key employees and outside directors; provided, however, that no more than 467 shares of common stock may be used for awards other than stock options. Stock options may be granted at prices not less than the fair market value at the date of grant and expire no later than ten years after the date of grant.
Restricted stock awards granted in the three-month periods ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 were 59 and 82, respectively. Restricted shares of 30 and 43 granted to officers in fiscal 2018 and fiscal 2017, respectively, vest 100% on the third anniversary of the grant date subject to the satisfaction of the performance metrics for the applicable three-year period. Restricted shares of 22 and 31 granted to officers and key employees in fiscal 2018 and fiscal 2017, respectively, vest 33⅓% per year over a three-year term.
9
Restricted shares of 7 and 8 granted to directors in fiscal 2018 and fiscal 2017, respectively, vest 100% on the first year anniversary of the grant date. No stock option awards were granted in the three-month periods ended June 30, 2017 and 2016.
During the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, the Company recognized stock-based compensation (income) costs related to stock option and restricted stock awards of $(67) and $29, respectively. The income tax (expense) benefit recognized related to stock-based compensation was $(23) and $10 for the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively.
The Company has an Employee Stock Purchase Plan (the "ESPP"), which allows eligible employees to purchase shares of the Company's common stock at a discount of up to 15% of its fair market value on the (1) last, (2) first or (3) lower of the last or first day of the six-month offering period. A total of 200 shares of common stock may be purchased under the ESPP. During the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, the Company recognized stock-based compensation costs of $0 and $13, respectively, related to the ESPP and $0 and $5, respectively, of related tax benefits.
NOTE 7 – INCOME PER SHARE:
Basic income per share is computed by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding for the period. Diluted income per share is calculated by dividing net income by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding and, when applicable, potential common shares outstanding during the period. A reconciliation of the numerators and denominators of basic and diluted income per share is presented below:
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Basic income per share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Numerator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
935 |
|
|
$ |
85 |
|
|
Denominator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
9,748 |
|
|
|
9,675 |
|
|
Basic income per share |
|
$ |
.10 |
|
|
$ |
.01 |
|
|
Diluted income per share |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Numerator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
935 |
|
|
$ |
85 |
|
|
Denominator: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted average common shares outstanding |
|
|
9,748 |
|
|
|
9,675 |
|
|
Stock options outstanding |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
5 |
|
|
Weighted average common and potential common shares outstanding |
|
|
9,758 |
|
|
|
9,680 |
|
|
Diluted income per share |
|
$ |
.10 |
|
|
$ |
.01 |
|
Options to purchase a total of 11 and 54 shares of common stock were outstanding at June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively, but were not included in the above computation of diluted income per share given their exercise prices as they would not be dilutive upon issuance.
NOTE 8 – PRODUCT WARRANTY LIABILITY:
The reconciliation of the changes in the product warranty liability is as follows:
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Balance at beginning of period |
|
$ |
538 |
|
|
$ |
686 |
|
|
(Income) expense for product warranties |
|
|
(160 |
) |
|
|
166 |
|
|
Product warranty claims paid |
|
|
(87 |
) |
|
|
(158 |
) |
|
Balance at end of period |
|
$ |
291 |
|
|
$ |
694 |
|
10
Income of $160 for product warranties in the three months ended June 30, 2017 resulted from the reversal of provisions made that were no longer required due to lower claims experience.
The product warranty liability is included in the line item "Accrued expenses and other current liabilities" in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets.
NOTE 9 - CASH FLOW STATEMENT:
Interest paid was $3 and $2 in the three-month periods ended June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively. Income taxes paid for the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 were $140 and $43, respectively.
At June 30, 2017 and 2016, respectively, there were $8 and $0 of capital purchases that were recorded in accounts payable and are not included in the caption "Purchase of property, plant and equipment" in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
NOTE 10 – EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS:
The components of pension cost are as follows:
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Service cost |
|
$ |
149 |
|
|
$ |
150 |
|
|
Interest cost |
|
|
356 |
|
|
|
362 |
|
|
Expected return on assets |
|
|
(744 |
) |
|
|
(718 |
) |
|
Amortization of actuarial loss |
|
|
253 |
|
|
|
338 |
|
|
Net pension cost |
|
$ |
14 |
|
|
$ |
132 |
|
The Company made no contributions to its defined benefit pension plan during the three months ended June 30, 2017 and does not expect to make any contributions to the plan for the balance of fiscal 2018.
The components of the postretirement benefit cost are as follows:
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Interest cost |
|
$ |
6 |
|
|
$ |
6 |
|
|
Amortization of actuarial loss |
|
|
10 |
|
|
|
10 |
|
|
Net postretirement benefit cost |
|
$ |
16 |
|
|
$ |
16 |
|
The Company paid no benefits related to its postretirement benefit plan during the three months ended June 30, 2017. The Company expects to pay benefits of approximately $83 for the balance of fiscal 2018.
The Company self-funds the medical insurance coverage it provides to its U.S. based employees. The Company maintains a stop loss insurance policy in order to limit its exposure to claims. The liability of $100 and $174 on June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017, respectively, related to the self-insured medical plan is primarily based upon claim history and is included in the caption “Accrued compensation” as a current liability in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets.
NOTE 11 – COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES:
The Company has been named as a defendant in lawsuits alleging personal injury from exposure to asbestos allegedly contained in, or accompanying, products made by the Company. The Company is a co-defendant with numerous other defendants in these lawsuits and intends to vigorously defend itself against these claims. The claims in the Company’s current lawsuits are similar to those made in previous asbestos-related suits that named the Company as defendant, which either were dismissed when it was shown that the Company had not supplied products to the plaintiffs’ places of work or were settled for immaterial amounts.
As of June 30, 2017, the Company was subject to the claims noted above, as well as other legal proceedings and potential claims that have arisen in the ordinary course of business.
11
Although the outcome of the lawsuits, legal proceedings or potential claims to which the Company is, or may become, a party to cannot be determined and an estimate of the reasonably possible loss or range of loss cannot be made, management does not believe that the outcomes, either individually or in the aggregate, will have a material effect on the Company’s results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
NOTE 12 – INCOME TAXES:
The Company files federal and state income tax returns in several domestic and international jurisdictions. In most tax jurisdictions, returns are subject to examination by the relevant tax authorities for a number of years after the returns have been filed. The Company is subject to U.S. federal examination for the tax years 2014 through 2016 and examination in state tax jurisdictions for the tax years 2012 through 2016. The Company is subject to examination in the People’s Republic of China for tax years 2014 through 2016.
There was no liability for unrecognized tax benefits at either June 30, 2017 or March 31, 2017.
NOTE 13 – CHANGES IN ACCUMULATED OTHER COMPREHENSIVE LOSS:
The changes in accumulated other comprehensive loss by component for the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 are as follows:
|
|
|
Pension and Other Postretirement Benefit Items |
|
|
Foreign Currency Items |
|
|
Total |
|
|||
|
Balance at April 1, 2017 |
|
$ |
(8,439 |
) |
|
$ |
5 |
|
|
$ |
(8,434 |
) |
|
Other comprehensive income before reclassifications |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
170 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
170 |
|
|
Net current-period other comprehensive income |
|
|
170 |
|
|
|
54 |
|
|
|
224 |
|
|
Balance at June 30, 2017 |
|
$ |
(8,269 |
) |
|
$ |
59 |
|
|
$ |
(8,210 |
) |
|
|
|
Pension and Other Postretirement Benefit Items |
|
|
Foreign Currency Items |
|
|
Total |
|
|||
|
Balance at April 1, 2016 |
|
$ |
(10,932 |
) |
|
$ |
256 |
|
|
$ |
(10,676 |
) |
|
Other comprehensive income before reclassifications |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
(138 |
) |
|
|
(138 |
) |
|
Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
|
225 |
|
|
|
— |
|
|
|
225 |
|
|
Net current-period other comprehensive income |
|
|
225 |
|
|
|
(138 |
) |
|
|
87 |
|
|
Balance at June 30, 2016 |
|
$ |
(10,707 |
) |
|
$ |
118 |
|
|
$ |
(10,589 |
) |
The reclassifications out of accumulated other comprehensive loss by component for the three months ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 are as follows:
|
Details about Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss Components |
|
Amount Reclassified from Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
|
|
|
Affected Line Item in the Condensed Consolidated Statements of Income and Retained Earnings |
||||||
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
|
2016 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
Pension and other postretirement benefit items: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amortization of actuarial loss |
|
$ |
(263 |
) |
(1) |
|
$ |
(348 |
) |
(1) |
|
Income before provision for income taxes |
|
|
|
|
(93 |
) |
|
|
|
(123 |
) |
|
|
Provision for income taxes |
|
|
|
$ |
(170 |
) |
|
|
$ |
(225 |
) |
|
|
Net income |
12
|
(1) |
These accumulated other comprehensive loss components are included within the computation of pension and other postretirement benefit costs. See Note 10. |
NOTE 14 – RESTRUCTURING CHARGE:
In the first quarter of fiscal 2017, the Company’s workforce was aligned with market conditions by eliminating certain management, office and manufacturing positions. As a result, a restructuring charge of $555 was recognized, which included severance and related employee benefit costs. This charge was included in the caption “Restructuring Charge” in the Condensed Consolidated Statement of Income and Retained Earnings for the three months ended June 30, 2016 The reconciliation of the changes in the restructuring reserve is as follows:
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|
June 30, |
|
||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Balance at beginning of period |
|
$ |
120 |
|
|
$ |
74 |
|
|
Expense for restructuring |
|
|
— |
|
|
|
555 |
|
|
Amounts paid for restructuring |
|
|
(28 |
) |
|
|
(77 |
) |
|
Balance at end of period |
|
$ |
92 |
|
|
$ |
552 |
|
The liability of $92 and $120 at June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017 respectively, are included in the caption “Accrued Compensation” in the Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets. June 30, 2017
NOTE 15 – ACCOUNTING AND REPORTING CHANGES:
In the normal course of business, management evaluates all new accounting pronouncements issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”), the Securities and Exchange Commission, the Emerging Issues Task Force, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants or any other authoritative accounting bodies to determine the potential impact they may have on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
In May 2014, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update ("ASU") 2014-09, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers." This guidance establishes principles for reporting information about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from a company’s contracts with customers. The guidance requires companies to apply a five-step model when recognizing revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods and services. The guidance also includes a comprehensive set of disclosure requirements regarding revenue recognition. The guidance allows two methods of adoption: (1) a full retrospective approach where historical financial information is presented in accordance with the new standard and (2) a modified retrospective approach where the guidance is applied to the most current period presented in the financial statements. In August 2015, the FASB issued ASU No 2015-14 "Revenue from Contracts with Customers: Deferral of the Effective Date," which deferred the effective date of ASU 2014-09 to annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2017, with earlier application permitted as of annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2016. In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-08, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Principal versus Agent Considerations (Reporting Revenue Gross versus Net)," to clarify the implementation guidance on principal versus agent. In April 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-10, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Identifying Performance Obligations and Licensing," which clarifies the identifying performance obligations and licensing implementation guidance. In May 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-12, "Revenue from Contracts with Customers (Topic 606): Narrow Scope Improvements and Practical Expedients," which clarifies the implementation guidance related to collectability, presentation of sales tax, noncash consideration, contract modifications and completed contracts at transition. The Company plans to adopt these standards using the modified retrospective approach in the first quarter of its fiscal year ending March 31, 2019, however, the method of adoption is subject to change as the Company progresses through the transition. The Company has developed a project plan and is currently reviewing its contracts and evaluating the impact of the guidance on its revenue. The Company currently believes that the most significant impact of adopting the guidance is the timing of revenue recognition. The Company believes that revenue on the majority of its contracts will continue to be recognized upon shipment while revenue on its larger contracts will be recognized over time as these contracts meet specific criteria established in the new standards. The Company is in the process of implementing changes to its business processes, systems and controls to support the recognition and disclosure requirements under the new guidance. See Note 2 for a description of the Company’s current revenue recognition policy.
13
In July 2015, the FASB issued ASU No. 2015-11, "Simplifying the Measurement of Inventory," which simplifies the subsequent measurement of inventory by requiring inventory to be measured at the lower of cost and net realizable value. Net realizable value is the estimated selling prices in the ordinary course of business, less reasonably predictable costs of completion, disposal, and transportation. This ASU is effective for public business entities for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company adopted the new guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2018. The adoption of this ASU did not have a material impact on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In February 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-02, "Leases (Topic 842)," which requires companies to recognize all leases as assets and liabilities on the consolidated balance sheet. This ASU retains a distinction between finance leases and operating leases, and the classification criteria for distinguishing between finance leases and operating leases are substantially similar to the classification criteria for distinguishing between capital leases and operating leases in the current accounting guidance. As a result, the effect of leases on the consolidated statement of comprehensive income and the consolidated statement of cash flows is largely unchanged from previous generally accepted accounting principles. The amendments in this ASU are effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2018, including interim periods within those fiscal years. Earlier application is permitted. The Company believes the adoption of this ASU may have a material impact on its assets and liabilities due to the addition of right-of-use assets and lease liabilities to its Consolidated Balance Sheet, however, it does not expect the guidance to have a material impact on its Consolidated Statement of Income or Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
In March 2016, the FASB issued ASU 2016-09, "Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718): Improvements to Employee Share-Based Payment Accounting." ASU 2016-09 changes how companies account for certain aspects of share-based payment awards to employees, including the accounting for income taxes, forfeitures and statutory tax withholding requirements, as well as classification in the statement of cash flows. ASU 2016-09 is effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, including interim periods within those annual periods. The Company adopted the new guidance in the first quarter of fiscal 2018. The adoption of this ASU did not have a material impact on the Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements.
In August 2016, the FASB issued ASU No. 2016-15, "Statement of Cash Flows (Topic 230)," which clarifies the presentation and classification of eight specific issues on the cash flow statement. This ASU is effective for public businesses for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company does not expect the adoption of this ASU will have a material effect on its Consolidated Financial Statements.
In March 2017, the FASB issued ASU No. 2017-07, "Compensation-Retirement Benefits (Topic 715)," which amended its guidance related to the presentation of net periodic pension cost and net periodic postretirement benefit cost. The amended guidance requires the service cost component be disaggregated from the other components of net benefit cost. The service cost component of expense is required to be reported in the income statement in the same line item as other compensation costs within income from operations. The other components of net benefit cost are required to be presented separately from the service cost component outside of income from operations. This ASU is effective for public businesses for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2017, and interim periods within those fiscal years. The Company is currently evaluating the impact that the adoption of this ASU will have on its Consolidated Financial Statements.
Management does not expect any other recently issued accounting pronouncements, which have not already been adopted, to have a material impact on the Company's consolidated financial statements.
14
Item 2.Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
(Dollar amounts in thousands, except per share data)
Overview
We are a global business that designs, manufactures and sells critical equipment for the energy, defense and chemical/ petrochemical industries. Our energy markets include oil refining, cogeneration, nuclear and alternative power. For the defense industry, our equipment is used in nuclear propulsion power systems for the U.S. Navy. For the chemical and petrochemical industries, our equipment is used in fertilizer, ethylene, methanol and downstream chemical facilities.
Graham’s global brand is built upon our world-renowned engineering expertise in vacuum and heat transfer technology, responsive and flexible service and high quality standards. We design and manufacture custom-engineered ejectors, vacuum pumping systems, surface condensers and vacuum systems. We are also a leading nuclear code accredited fabrication and specialty machining company. We supply components used inside reactor vessels and outside containment vessels of nuclear power facilities. Our equipment can also be found in other diverse applications such as metal refining, pulp and paper processing, water heating, refrigeration, desalination, food processing, pharmaceutical, heating, ventilating and air conditioning.
Our corporate headquarters are located in Batavia, New York. We have production facilities co-located with our headquarters in Batavia and also at our wholly-owned subsidiary, Energy Steel & Supply Co. ("Energy Steel"), located in Lapeer, Michigan. We also have a wholly-owned foreign subsidiary, Graham Vacuum and Heat Transfer Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. ("GVHTT"), located in Suzhou, China. GVHTT provides sales and engineering support for us in the People’s Republic of China and management oversight for our operations throughout Southeast Asia.
Our current fiscal year (which we refer to as "fiscal 2018") ends March 31, 2018.
Highlights
Highlights for the three months ended June 30, 2017 include:
|
|
• |
Net sales for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $20,851 down 7% compared with $22,365 for the first quarter of the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 (we refer to the fiscal year ended March 31, 2017 as "fiscal 2017"). |
|
|
• |
Net income and income per diluted share for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $935 and $0.10, compared with $85 and $0.01, respectively, for the first quarter of fiscal 2017. Excluding a restructuring charge, net income and income per diluted share for the first quarter of the prior year, fiscal 2017, were $468 and $0.05. |
|
|
• |
Orders booked in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $11,064, down 24% compared with the first quarter of fiscal 2017 when orders were $14,601. |
|
|
• |
Backlog was $72,908 at June 30, 2017, compared with $82,590 at March 31, 2017. |
|
|
• |
Gross profit margin and operating margin for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were 23% and 6%, respectively, compared with 18% and 0%, respectively, for the first quarter of fiscal 2017. |
|
|
• |
Cash and short-term investments at June 30, 2017 were $75,260, compared with $73,474 on March 31, 2017. |
Forward-Looking Statements
This report and other documents we file with the Securities and Exchange Commission include "forward-looking statements" within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
These statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause actual results to be materially different from any future results implied by the forward-looking statements. Such factors include, but are not limited to, the risks and uncertainties identified by us under the heading "Risk Factors" in Item 1A of our Annual Report on Form 10-K for fiscal 2017.
Forward-looking statements may also include, but are not limited to, statements about:
|
|
• |
the current and future economic environments affecting us and the markets we serve; |
|
|
• |
expectations regarding investments in new projects by our customers; |
15
|
|
• |
expectations regarding achievement of revenue and profitability expectations; |
|
|
• |
plans for future products and services and for enhancements to existing products and services; |
|
|
• |
our operations in foreign countries; |
|
|
• |
political instability in regions in which our customers are located; |
|
|
• |
our ability to affect our growth and acquisition strategy; |
|
|
• |
our ability to expand nuclear power work into new markets; |
|
|
• |
our ability to maintain or expand nuclear power work for the U.S. Navy; |
|
|
• |
our ability to successfully execute our existing contracts; |
|
|
• |
estimates regarding our liquidity and capital requirements; |
|
|
• |
timing of conversion of backlog to sales; |
|
|
• |
our ability to attract or retain customers; |
|
|
• |
the outcome of any existing or future litigation; and |
|
|
• |
our ability to increase our productivity and capacity. |
Forward-looking statements are usually accompanied by words such as "anticipate," "believe," "estimate," "may," "might," "intend," "interest," "appear," "expect," "suggest," "plan," "encourage," "potential", “view” and similar expressions. Actual results could differ materially from historical results or those implied by the forward-looking statements contained in this report.
Undue reliance should not be placed on our forward-looking statements. Except as required by law, we undertake no obligation to update or announce any revisions to forward-looking statements contained in this report, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
Current Market Conditions
Our global energy markets continue to be contracted. This is caused by crude oil and natural gas price declines, price volatility and near term price uncertainty. In response, our customers in the downstream energy sector sharply reduced capital spending for new capacity, revamping and turnaround for routine maintenance. Additionally, the nuclear market capital spending for both new capacity and to maintain existing facilities has dramatically shifted downward. It is down 25% to 35% compared with 3 to 4 years ago according to a report from the Nuclear Energy Institute. The contracted capital spending within the energy and nuclear markets has had the effect of measurably reducing new orders and consequently reducing sales.
For both the energy and nuclear markets these current conditions present challenges. The long term view for these end markets, however, is that fundamentals will drive increasing demand. These fundamentals include rising populations, strong emerging market economic growth, and overall global economic expansion, which will result in capital investment to satisfy increasing global demand.
Our naval nuclear propulsion market has demand tied to aircraft carrier and submarine vessel construction schedules of the primary shipyards who service the U.S. Navy. We expect growth in our naval nuclear propulsion business based on our strategic actions to increase our market share and expected demand. For more information, refer to the heading “Strategy and Outlook” within this Item 2 of this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q
We believe the long-term outlook in our key markets supports our strategy. In the near term, new order levels are expected to remain volatile, resulting in both relatively strong and weak periods.
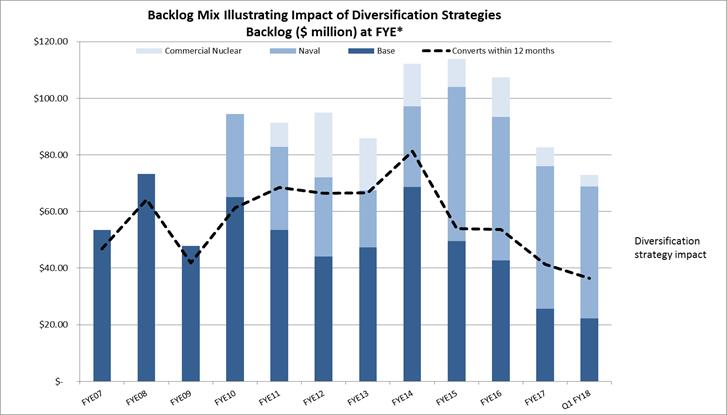
The chart below shows the impact of our diversification strategy. Nearly 70% of our current backlog is from markets not served in the Fiscal 2007-2009 time frame.
16
*fiscal year ended March 31
Results of Operations
To better understand the significant factors that influenced our performance during the periods presented, the following discussion should be read in conjunction with our Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements and the notes to our Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part I, Item 1, of this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q.
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
Three Months Ended |
|
|||||
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|||||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2016 |
|
||
|
Net sales |
|
$ |
20,851 |
|
|
$ |
22,365 |
|
|
Gross profit |
|
$ |
4,866 |
|
|
$ |
4,111 |
|
|
Gross profit margin |
|
|
23 |
% |
|
|
18 |
% |
|
SG&A expense (1) |
|
$ |
3,681 |
|
|
$ |
3,656 |
|
|
SG&A as a percent of sales |
|
|
18 |
% |
|
|
16 |
% |
|
Net income |
|
$ |
935 |
|
|
$ |
85 |
|
|
Diluted income per share |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.01 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
147,531 |
|
|
$ |
148,043 |
|
|
Total assets excluding cash, cash equivalents and investments |
|
$ |
72,271 |
|
|
$ |
80,338 |
|
|
|
(1) |
Selling, general and administrative expense is referred to as "SG&A". |
The First Quarter of Fiscal 2018 Compared With the First Quarter of Fiscal 2017
Sales for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $20,851, a 7% decrease from sales of $22,365 for the first quarter of fiscal 2017. Our domestic sales, as a percentage of aggregate sales, were 71% in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 compared with 73% in the first quarter of fiscal 2017. Domestic sales decreased $1,425, or 9% year-over-year. International sales decreased $89, or 1%, in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 compared with the first quarter of fiscal 2017, driven by decreases in South America mostly offset by increases in Canada and Asia. Sales in the three months ended June 30, 2017 were 18% to the refining industry, 34% to the chemical and
17
petrochemical industries, 19% to the power industry, including the nuclear market, and 29% to other commercial and industrial applications, including the U.S. Navy. Sales in the three months ended June 30, 2016 were 32% to the refining industry, 23% to the chemical and petrochemical industries, 21% to the power industry, including the nuclear market, and 24% to other commercial and industrial applications, including the U.S. Navy. Fluctuation in sales among markets, products and geographic locations varies, sometimes significantly, from quarter-to-quarter based on timing and magnitude of projects. See also "Current Market Conditions," above. For additional information on anticipated future sales and our markets, see "Orders and Backlog" below.
Our gross profit margin for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 was 23% compared with 18% for the first quarter of fiscal 2017. Gross profit for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 increased 18% compared with fiscal 2017, to $4,866 from $4,111. Gross profit and margin were favorably impacted by project mix and timing of overhead costs.
SG&A expenses as a percent of sales for the three month periods ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 were 18% and 16%, respectively. SG&A expenses in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $3,681, an increase of $25, or 1%, compared with the first quarter of fiscal 2017 SG&A of $3,656. See Note 14 to our Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements included in Part I, Item 1, of this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q.
In the first quarter of fiscal 2017, we incurred a pre-tax restructuring charge of $555 ($383 after tax) for severance costs related to certain headcount reductions.
Interest income for the three month periods ended June 30, 2017 and 2016 was $151 and $87, respectively. Interest expense was $3 for the quarter ended June 30, 2017 compared with $2 for the quarter ended June 30, 2016.
Our tax rate in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 was 30%. In the first quarter of fiscal 2017, we recognized a $100 tax benefit from a favorable tax adjustment.
Net income and income per diluted share for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $935 and $0.10, compared with $85 and $0.01, respectively, for the first quarter of fiscal 2017. Excluding a restructuring charge, net income and income per diluted share for the first quarter of fiscal 2017 were $468 and $0.05.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our Condensed Consolidated Balance Sheets and Statements of Cash Flows:
|
|
|
June 30, |
|
|
March 31, |
|
||
|
|
|
2017 |
|
|
2017 |
|
||
|
Cash and investments |
|
$ |
75,260 |
|
|
$ |
73,474 |
|
|
Working capital |
|
|
79,150 |
|
|
|
78,688 |
|
|
Working capital ratio(1) |
|
|
3.9 |
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
|
Working capital excluding cash and investments |
|
|
3,890 |
|
|
|
5,214 |
|
|
|
(1) |
Working capital ratio equals current assets divided by current liabilities. |
Net cash generated by operating activities for the first quarter of fiscal 2018 was $2,876, compared with $3,814 of cash generated for the first quarter of fiscal 2017. The decrease in cash generation year over year was attributable to timing of customer deposits, and accounts payable and inventory levels, partially offset by higher net income and accounts receivable and unbilled revenue.
Dividend payments and capital expenditures in the first quarter of fiscal 2018 were $879 and $117, respectively, compared with $866 and $129, respectively, for the first quarter of fiscal 2017.
Capital expenditures for fiscal 2018 are expected to be between approximately $2,500 and $3,000. Approximately 80% of our fiscal 2018 capital expenditures are expected to be for machinery and equipment, with the remaining amounts expected to be used for other items.
Cash and investments were $75,260 on June 30, 2017 compared with $73,474 on March 31, 2017, up $1,786.
We invest net cash generated from operations in excess of cash held for near-term needs in short-term, less than 365 days, certificates of deposit, money market accounts or U.S. government instruments, generally with maturity periods of up to 180 days.
18
Our money market account is used to securitize our outstanding letters of credit, which reduces our cost on those letters of credit. Approximately 95% of our cash and investments are held in the U.S. The remaining 5% is invested in our China operations.
Our revolving credit facility with JP Morgan Chase provides us with a line of credit of $25,000, including letters of credit and bank guarantees. In addition, our JP Morgan Chase agreement allows us to increase the line of credit, at our discretion, up to another $25,000, for total availability of $50,000. Borrowings under this credit facility are secured by all of our assets. We also have a $5,000 unsecured line of credit with HSBC, N.A. Letters of credit outstanding on June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017 were $9,603 and $8,372, respectively. The outstanding letters of credit as of June 30, 2017 were issued by JP Morgan Chase, HSBC, as well as Bank of America, under our previous credit facility. There were no other amounts outstanding on our credit facilities at June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017. The borrowing rate under our JP Morgan Chase facility as of June 30, 2017 was the bank’s prime rate, or 4.25%. Availability under the JP Morgan Chase and HSBC lines of credit was $24,279 and $25,761 at June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017, respectively. We believe that cash generated from operations, combined with our investments and available financing capacity under our credit facility, will be adequate both to meet our cash needs for the immediate future and to support our growth strategies.
Orders and Backlog
Orders for the three-month period ended June 30, 2017 were $11,064 compared with $14,601 for the same period last year, a decrease of 24%. Orders represent written communications received from customers requesting us to supply products and/or services. Domestic orders were 77% of total orders, or $8,466, and international orders were 23% of total orders, or $2,598, in the current quarter compared with the first quarter of fiscal 2017, when domestic orders were 72%, or $10,547, of total orders, and international orders were 28%, or $4,054, of total orders.
Backlog was $72,908 at June 30, 2017, compared with $82,590 at March 31, 2017, a 12% decrease. Backlog is defined as the total dollar value of orders received for which revenue has not yet been recognized. Approximately 45% to 55% of orders currently in our backlog are expected to be converted to sales within one year. The majority of the orders that convert beyond twelve months are for the U.S. Navy. At June 30, 2017, 18% of our backlog was attributable to equipment for refinery project work, 9% for chemical and petrochemical projects, 6% for power projects, including nuclear, 64% for U.S. Navy projects and 3% for other industrial applications. This split of backlog by end market is comparable to the levels on March 31, 2017. At June 30, 2016, 20% of our backlog was attributed to equipment for refinery project work, 10% for chemical and petrochemical projects, 16% for power projects, 50% for U.S. Navy projects and 4% for other industrial applications. At June 30, 2017, we had no projects on hold.
Strategy and Outlook
Ongoing weakness in the global energy markets is expected to continue to negatively impact our business in fiscal 2018. The decrease in requests for quotations and orders, as well as multiple cancellations which occurred over the last ten quarters are expected to result in a challenging fiscal 2018. Our pipeline has contracted as our oil refining and chemical market customers have further reduced their capital spending plans when compared with last year. We believe these reductions by our customers are in reaction to continued low and volatile oil prices. The expected duration of this downturn is uncertain.
Despite the current downturn, we continue to believe in the long-term potential of the energy markets we serve. We intend to expand our participation and market share. As a result of our diversification strategy with the U.S. Navy and the power market, we believe this long-term strength will support our strategy to significantly grow our business when the energy markets recover. We have invested in capacity to serve our commercial customers as well as to expand the work we do for the U.S. Navy. We continue to look for organic growth opportunities as well as acquisitions or other business combinations that we believe will allow us to expand our presence in both our existing and ancillary markets. We are focused on reducing earnings volatility, growing our business and further diversifying our business and product lines.
The headwinds in the energy markets are causing near-term uncertainty. This has affected our outlook for fiscal 2018. We expect revenue in fiscal 2018 to be approximately $80,000 to $90,000. We project that approximately 45% to 55% of our March 31, 2017 backlog will convert to sales in fiscal 2018. We expect the remaining backlog will convert beyond fiscal 2018, which includes a combination of U.S. Navy orders that have a long conversion cycle (up to five years) as well as certain commercial orders for which the conversion has been extended by our customers.
We expect gross profit margin in fiscal 2018 to be in the 22% to 24% range, compared with 24% to 26% in the past two fiscal years. We expect continued pricing pressure and under-utilization of our production facilities in fiscal 2018. We believe that production overhead absorption will be weak, which we expect in turn will put continued pressure on gross profit margins.
SG&A during fiscal 2018 is expected to be between $16,000 and $17,000. Our effective tax rate during fiscal 2018 is expected to be between 30% and 32%.
19
We expect that cash flow in fiscal 2018 will be much more moderate than fiscal 2017. Fiscal 2017 cash flow benefited from the continued build-up of customer deposits.
We will continue to look toward future growth while being mindful of near term profitability, given short-term challenges.
Contingencies and Commitments
We have been named as a defendant in lawsuits alleging personal injury from exposure to asbestos allegedly contained in or accompanying our products. We are a co-defendant with numerous other defendants in these lawsuits and intend to vigorously defend ourselves against these claims. The claims in our current lawsuits are similar to those made in previous asbestos lawsuits that named us as a defendant. Such previous lawsuits either were dismissed when it was shown that we had not supplied products to the plaintiffs’ places of work or were settled by us for immaterial amounts.
As of June 30, 2017, we are subject to the claims noted above, as well as other legal proceedings and potential claims that have arisen in the ordinary course of business. Although the outcome of the lawsuits, legal proceedings or potential claims to which we are or may become a party cannot be determined and an estimate of the reasonably possible loss or range of loss cannot be made, we do not believe that the outcomes, either individually or in the aggregate, will have a material effect on our results of operations, financial position or cash flows.
Critical Accounting Policies, Estimates, and Judgments
Our unaudited condensed consolidated financial statements are based on the selection of accounting policies and the application of significant accounting estimates, some of which require management to make significant assumptions. We believe that the most critical accounting estimates used in the preparation of our condensed consolidated financial statements relate to labor hour estimates and establishment of operational milestones which are used to recognize revenue under the percentage-of-completion method, fair value estimates of identifiable tangible and intangible assets acquired in business combinations, accounting for contingencies, under which we accrue a loss when it is probable that a liability has been incurred and the amount can be reasonably estimated, and accounting for pensions and other postretirement benefits. For further information, refer to Item 7 "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and Item 8 "Financial Statements and Supplementary Data" included in our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2017.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have any off balance sheet arrangements as of June 30, 2017 or March 31, 2017, other than operating leases and letters of credit.
Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
The principal market risks (i.e., the risk of loss arising from market changes) to which we are exposed are foreign currency exchange rates, price risk and project cancellation risk.
The assumptions applied in preparing the following qualitative and quantitative disclosures regarding foreign currency exchange rate, price risk and project cancellation risk are based upon volatility ranges experienced by us in relevant historical periods, our current knowledge of the marketplace, and our judgment of the probability of future volatility based upon the historical trends and economic conditions of the markets in which we operate.
Foreign Currency
International consolidated sales for the first three months of fiscal 2018 were 29% of total sales compared with 27% for the same period of fiscal 2017. Operating in markets throughout the world exposes us to movements in currency exchange rates. Currency movements can affect sales in several ways, the foremost being our ability to compete for orders against foreign competitors that base their prices on relatively weaker currencies. Business lost due to competition for orders against competitors using a relatively weaker currency cannot be quantified. In addition, cash can be adversely impacted by the conversion of sales made by us in a foreign currency to U.S. dollars. In each of the first three months of fiscal 2018 and fiscal 2017, all sales by us and our wholly-owned subsidiaries, for which we were paid, were denominated in the local currency of the respective subsidiary (U.S. dollars or Chinese RMB).
We have limited exposure to foreign currency purchases. In each of the first three months of fiscal 2018 and 2017, our purchases in foreign currencies represented approximately 1% of the cost of products sold. At certain times, we may enter into forward foreign currency exchange agreements to hedge our exposure against potential unfavorable changes in foreign currency values on significant sales and purchase contracts negotiated in foreign currencies. Forward foreign currency exchange contracts were
20
not used in the periods being reported on in this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q and as of June 30, 2017 and March 31, 2017, we held no forward foreign currency contracts.
Price Risk
Operating in a global marketplace requires us to compete with other global manufacturers which, in some instances, benefit from lower production costs and more favorable economic conditions. Although we believe that our customers differentiate our products on the basis of our manufacturing quality, responsive and flexible service, and engineering experience and excellence, among other things, such lower production costs and more favorable economic conditions mean that certain of our competitors are able to offer products similar to ours at lower prices. In market downturns, such as we are currently experiencing, we typically see depressed price levels. Moreover, the cost of metals and other materials used in our products have experienced significant volatility. Such factors, in addition to the global effects of the ongoing volatility and disruption of the capital and credit markets, have resulted in downward demand for and pricing pressure on our products.
Project Cancellation and Project Continuation Risk
Open orders are reviewed continuously through communications with customers. If it becomes evident to us that a project is delayed well beyond its original shipment date, management will move the project into "placed on hold" (i.e., suspended) category. Furthermore, if a project is cancelled by our customer, it is removed from our backlog. We attempt to mitigate the risk of cancellation by structuring contracts with our customers to maximize the likelihood that progress payments made to us for individual projects cover the costs we have incurred. As a result, we do not believe we have a significant cash exposure to projects which may be cancelled. At June 30, 2017, we had no projects on hold.
Item 4.Controls and Procedures
Conclusion regarding the effectiveness of disclosure controls and procedures
Our President and Chief Executive Officer (principal executive officer) and Vice President-Finance & Administration and Chief Financial Officer (principal financial officer) each have evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e)) as of the end of the period covered by this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q. Based on such evaluation, and as of such date, our President and Chief Executive Officer and Vice President-Finance & Administration and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective in all material respects.
Changes in internal control over financial reporting
There has been no change to our internal control over financial reporting during the quarter covered by this Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q that has materially affected, or that is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
21
GRAHAM CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
FORM 10-Q
JUNE 30, 2017
PART II - OTHER INFORMATION
Item 2.Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds
Purchase of Equity Securities by the Issuer
During the first quarter of fiscal 2018, we directly withheld shares for tax withholding purposes from restricted stock awarded to officers that vested during the period. Common stock repurchases in the quarter ended June 30, 2017 were as follows:
|
Period |
|
Total Number of Shares Purchased |
|
Average Price Paid Per Share |
|
Total Number of Shares Purchased as Part of Publically Announced Program |
|
Maximum Number of Shares That May Yet Be Purchased Under the Program |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4/01/2017 – 4/30/2017 |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
5/01/2017 – 5/31/2017 |
|
6 |
|
$21.76 |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
6/01/2017 – 6/30/2017 |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
-- |
|
Total |
|
6 |
|
$21.76 |
|
-- |
|
-- |
Item 5.Other Information
The below disclosure is being made pursuant to the instruction contained in Item 5 of Form 10-Q. The item number below refers to the applicable Current Report on Form 8-K Item numbers.
Item 5.07 Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders.
At our Annual Meeting of Stockholders held on August 3, 2017, our stockholders voted on the matters described below.
|
|
1. |
Our stockholders elected two directors, each for a three-year term expiring at the Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held in 2020. The number of shares that (i) voted for the election of each such director; (ii) withheld authority to vote for each such director; and (iii) represented broker non-votes with respect to each such director is summarized in the table below. |
|
Director Nominee |
|
Votes For |
|
Votes Withheld |
|
Broker Non-Votes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
James J. Barber, Ph.D. |
|
7,426,010 |
|
129,998 |
|
1,528,459 |
|
Gerard T. Mazurkiewicz |
|
7,123,886 |
|
432,122 |
|
1,528,459 |
|
|
2. |
On an advisory basis, our stockholders approved the compensation of our named executive officers as such compensation information is disclosed in our definitive proxy statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on June 22, 2017, including the Compensation Discussion and Analysis, compensation tables and other narrative disclosures included therein. The table below summarizes the number of shares that voted for, against, and abstained from voting on the compensation of our named executive officers, as well as the number of shares representing broker non-votes with respect to such advisory vote. |
|
Votes For |
|
Votes Against |
|
Abstentions |
|
Broker Non-Votes |
|
7,358,064 |
|
179,714 |
|
18,230 |
|
1,528,459 |
22
|
|
3. |
On an advisory basis, our stockholders approved the frequency at which an advisory vote on the compensation of our named executive officers, as included in item 2 above, should occur. The table below summarizes the number of shares that voted for a frequency of one year, two years, three years, and abstained from voting, as well as the number of shares representing broker non-votes with respect to such vote. |
|
One Year |
|
Two Years |
|
Three Years |
|
Abstentions |
Broker Non-Votes |
|
6,311,639 |
|
9,392 |
|
1,222,943 |
|
12,034 |
1,528,459 |
|
|
4. |
Our stockholders ratified the selection of Deloitte & Touche LLP as our independent registered public accounting firm for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2018. The number of shares that voted for, against, and abstained from voting for the ratification of the selection of Deloitte & Touche LLP as our independent registered public accounting firm for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2018 is summarized in the table below. |
|
Votes For |
|
Votes Against |
|
Abstentions |
|
8,785,328 |
|
283,829 |
|
15,310 |
See index to exhibits on page 25 of this report.
23
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
GRAHAM CORPORATION
|
||
|
By: |
|
|
/s/ Jeffrey Glajch |
|
|
|
|
Jeffrey Glajch |
|
|
|
|
Vice President-Finance & Administration and |
|
|
|
|
Chief Financial Officer |
Date: August 7, 2017
24
|
(10) |
|
Material Contracts |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
|
10.1 |
Compensation information, including information regarding stock option and restricted stock grants made to the Company's named executive officers under the 2000 Amended and Restated Graham Corporation Incentive Plan to Increase Shareholder Value and named executive officer cash bonus information, previously filed on the Company's Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 31, 2017, is incorporated herein by reference. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
|
10.2 |
Graham Corporation Annual Stock-Based Long-Term Incentive Award Plan for Senior Executives in effect for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2018, previously filed as Exhibit 99.1 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 31, 2017, is incorporated herein by reference. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
# |
|
10.3 |
Graham Corporation Annual Executive Cash Bonus Program in effect for the fiscal year ending March 31, 2018, previously filed as Exhibit 99.2 to the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K dated May 31, 2017, is incorporated herein by reference. |
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
(31) |
|
Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certifications |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
31.1 |
Certification of Principal Executive Officer |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
31.2 |
Certification of Principal Financial Officer |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
(32) |
|
Section 1350 Certification |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
32.1 |
Section 1350 Certifications |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
(101) |
|
Interactive Date File |
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
101.INS |
XBRL Instance Document |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
101.SCH |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
101.CAL |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
101.DEF |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
101.LAB |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
+ |
|
101.PRE |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
+
# |
Exhibit filed with this report
Management contract or compensation plan |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|||||
25